The Ultimate Guide to Self-Employment Tax Write-Offs: Don't Leave Money on the Table!
Why Self-Employment Tax Deductions Matter for Your Bottom Line

Self employment tax deductions are write-offs that reduce your taxable income when you work for yourself. If you're a sole proprietor, freelancer, or gig worker, you can deduct ordinary and necessary business expenses, lowering both your income tax and self-employment tax bills.
Quick Answer: Most Common Self-Employment Tax Deductions
- Self-employment tax deduction – Deduct 50% of your SE tax.
- Home office – Write off a portion of rent, utilities, and repairs for a dedicated workspace.
- Vehicle expenses – Deduct 70 cents per mile (2025 rate) or actual costs.
- Health insurance premiums – Deduct 100% if not eligible for an employer plan.
- Retirement contributions – SEP IRA, Solo 401(k), or SIMPLE IRA contributions.
- Business supplies – Computers, software, and tools used for work.
- Professional fees – Legal, accounting, and bookkeeping services.
- Advertising – Website hosting, ads, and business cards.
- Travel and meals – Business travel and 50% of meal costs.
Claiming these correctly can save you thousands. For example, earning $50,000 with $15,000 in deductions means you only pay taxes on $35,000. The IRS defines deductible expenses as "ordinary" (common in your field) and "necessary" (helpful for your business).
I'm Elias Park, founder of ENSA Pro Inc. Over the past three years, I've prepared over 2,000 tax returns annually for self-employed individuals across California. This guide walks you through every major deduction category to maximize your write-offs.
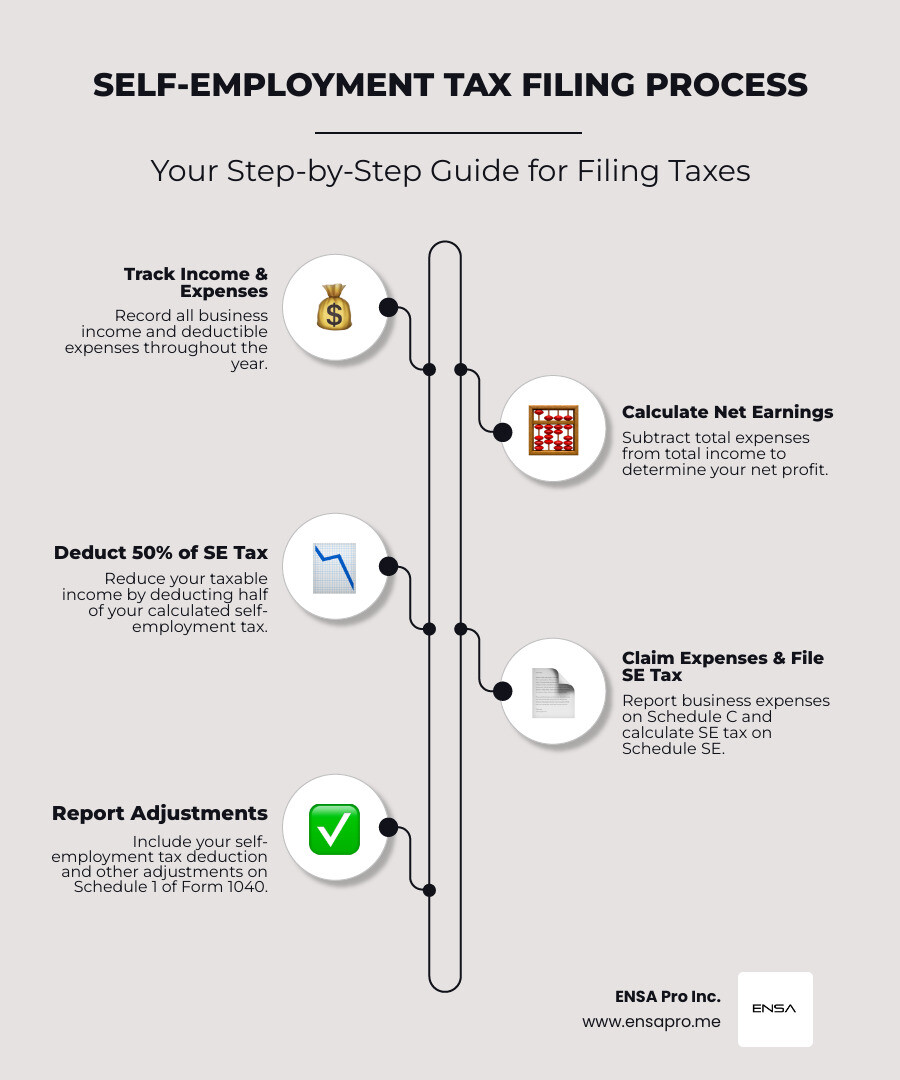
Understanding Self-Employment Tax and the 50% Deduction
If you're a sole proprietor or independent contractor, you're responsible for self-employment (SE) tax, covering Social Security and Medicare. Unlike employees, you pay both the employee and employer portions.

You pay SE tax if net earnings are $400 or more. The rate is 15.3% (12.4% for Social Security and 2.9% for Medicare). For 2025, the Social Security portion applies to the first $176,100 of earnings. There is no limit for Medicare. Some may also owe a 0.9% Additional Medicare Tax if income exceeds certain thresholds (e.g., $200,000 for single filers).
You can deduct 50% of the SE tax you pay on your individual income tax return. This deduction reduces your adjusted gross income (AGI) and is reported on Schedule 1 (Form 1040). For more details, see the IRS guidance on Self-Employment Taxes or use a Self-Employed Tax Deductions Worksheet.
How to calculate your self employment tax deductions
Start with your gross income and subtract ordinary business expenses. SE tax is calculated on 92.35% of your net profit. Once you determine the total SE tax using Schedule SE, you deduct 50% of that amount on Schedule 1. This reduces your income tax but doesn't lower the earnings used for Social Security benefit calculations. The Social Security Administration uses Schedule SE data to track your coverage.
Deducting health insurance and retirement contributions
You can generally deduct 100% of health insurance premiums for yourself, your spouse, and dependents if you aren't eligible for an employer-sponsored plan. This deduction is limited to your business's net profit and is taken on Schedule 1. For 2025, long-term care insurance deduction caps range from $480 to $6,020 based on age. Review IRS Tax Compliance for more.
Retirement contributions are also deductible:
- SEP IRA: Contribute up to 25% of net earnings.
- SIMPLE IRA: Ideal for small businesses with employees; allows employee and employer contributions.
- Solo 401(k): Offers high limits for business owners with no employees (except a spouse).
- Defined Benefit Plans: Suitable for high earners wanting to make large contributions.
These plans lower your current tax burden while building future security.
Maximizing Your Home Office and Vehicle Expenses
To qualify for the home office deduction, you must use a portion of your home exclusively and regularly for business. It must be your principal place of business or where you meet clients.
Two calculation methods exist:
- Simplified Option: Deduct $5 per square foot, up to 300 square feet ($1,500 max).
- Regular Method: Deduct a percentage of actual expenses (mortgage interest, utilities, insurance) based on the office's square footage relative to the whole home. Direct expenses, like office repairs, are 100% deductible.
Rent for dedicated offices or co-working spaces is fully deductible. Bookkeeping Services Irvine CA can help track these costs.
Vehicle mileage and actual self employment tax deductions
- Standard Mileage Rate: For 2025, the IRS’s standard mileage reimbursement rate is 70 cents per mile. This covers gas, repairs, and depreciation. Parking and tolls are extra. Use mileage tracking apps out there for records.
- Actual Expense Method: Track all costs (gas, insurance, lease). If you use the car 70% for business, deduct 70% of total costs.
Equipment, furniture, and tech write-offs
For computers, furniture, and tech gear, you have several deduction options:
- Section 179: Deduct the full price in the year of purchase. The 2025 limit is $2,500,000.
- Bonus Depreciation: Allows a 100% deduction for qualified property in 2025.
- Regular Depreciation: Spread the cost over the asset's useful life.
| Feature | Section 179 | Bonus Depreciation |
|---|---|---|
| Limit (2025) | $2,500,000 | 100% of cost |
| Taxable Income | Cannot create a net loss | Can create a net loss |
| Property Type | Specified business property | Broader range |
Software subscriptions and equipment rentals are also 100% deductible.
Essential Business Operations and Professional Expenses
Advertising and marketing costs, including online ads, website hosting, and branding, are fully deductible. See our guide on Tax Deductible Expenses for more.
Bank and merchant fees for business accounts and processors like Stripe are deductible. Professional fees for legal, accounting, and bookkeeping are also write-offs. Working with a Small Business Accountant Irvine ensures these are handled correctly.
Dues, memberships, and professional development are deductible if they improve skills for your current business. Licenses and permits are also eligible.
Travel, meals, and specialized business costs
Out-of-town travel (airfare, lodging) is 100% deductible. Meal expenses are generally 50% deductible and must be business-related. You can use per diem rates for travel within the U.S..
Startup costs: Deduct up to $5,000 in startup and $5,000 in organizational costs in your first year. This phases out if total costs exceed $50,000.
Contractor payments are deductible. If you pay a contractor $600+, you must usually file Form 1099-NEC. This is a core part of Business Tax Preparation Irvine.
Other deductions include:
- Supplies: Office and industry-specific materials.
- Shipping: Postage and delivery costs.
- Interest: On business loans or credit cards.
- Insurance: General liability and professional insurance.
Employee pay, benefits, and inventory costs
Salaries, benefits, and payroll taxes for employees are fully deductible. A sole proprietor's own salary is not a business expense.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Deduct the direct costs of products sold (Beginning Inventory + Purchases - Ending Inventory). Small businesses with receipts under $31 million (for 2025) may have simpler accounting. Visit SBA.gov for resources.
Charitable and gifts: Business gifts are limited to $25 per person per year. Volunteer expenses for charities can be itemized on Schedule A.
Frequently Asked Questions about Self-Employment Tax Deductions
Ordinary vs. Necessary Business Expenses
An ordinary expense is common in your industry. A necessary expense is helpful for your business. Both are reported on Schedule C.
Can I deduct work clothes and personal appearance expenses?
Generally, no, if they are suitable for everyday wear. Exceptions include protective gear, uniforms, or costumes not adaptable for general use. Professional makeup for stage or video may be deductible if used exclusively for business.
What is the Qualified Business Income (QBI) deduction?
The QBI deduction (Section 199A) allows eligible individuals to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income. Limitations apply for high earners and Specified Service Trade or Businesses (SSTBs) like law or accounting. Use Form 8995 to claim it.
How do I pay estimated taxes as a self-employed individual?
You must pay estimated taxes quarterly if you expect to owe $1,000 or more. Deadlines are April 15, June 15, September 15, and January 15. Use Form 1040-ES and pay via IRS Direct Pay or EFTPS.gov. Virtual Tax Preparation California can help ensure accuracy. See IRS Estimated Taxes for more.
Conclusion
Navigating self employment tax deductions can seem complex, but with the right knowledge and diligent record-keeping, you can significantly reduce your tax burden and keep more of your hard-earned money. From understanding your self-employment tax obligations and the valuable 50% deduction, to maximizing write-offs for your home office, vehicle, and essential business operations, every deduction counts.
The key to successful tax savings and audit protection lies in substantiating every deduction with accurate records, receipts, and invoices. This not only ensures compliance but also provides peace of mind.
At ENSA Pro Inc., we understand the unique challenges faced by self-employed individuals and small business owners in Irvine, Orange County, and throughout California. We offer personalized tax preparation services designed to uncover every eligible deduction, providing you with a free, no-obligation tax return draft and thorough IRS status checks. Our goal is to ensure you achieve the best possible tax outcome, year after year. Don't leave money on the table—let us help you maximize your self employment tax deductions. Contact us today for expert Tax Preparation Irvine CA.
